News Insights
Electric vehicles are no longer an emerging trend-they are a structural force reshaping global mobility, energy systems, and industrial policy. In 2025, electric vehicles accounted for more than 25% of new vehicle sales globally, with China surpassing the 50% mark and Europe recording months where EVs outsold internal combustion vehicles entirely.
As adoption accelerates, batteries have become the true strategic battleground. In 2026, the EV battery landscape will be defined by three forces: new chemistries entering commercial use, heightened geopolitical…
FAW Hongqi’s All-Solid-State Battery Prototype Signals a Breakthrough Moment for Next-Generation EVs
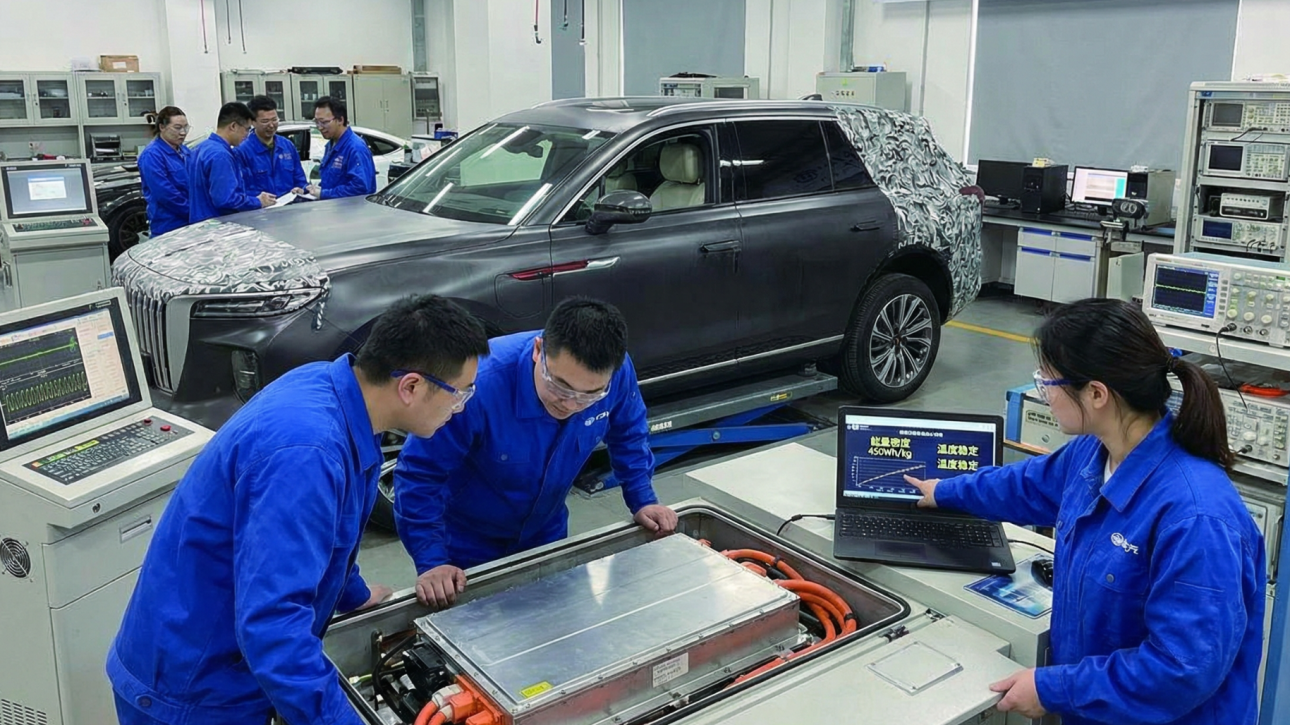
In January 2026, China FAW Group reached a pivotal milestone in the global race toward next-generation electric vehicle technology. The successful rollout of Hongqi’s first all-solid-state battery prototype vehicle marks the transition of solid-state innovation from laboratory research to real-world vehicle validation-a moment with far-reaching implications for the automotive and energy storage industries.
For global automotive executives, battery manufacturers, and technology investors, this development signals more than technical progress. It reflects a strategic inflection point in how future EV platforms…
Battery technology is entering a decisive phase. As electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and grid-scale electrification accelerate globally, incremental improvements to conventional lithium-ion batteries are no longer sufficient. The next wave of competitiveness will be defined by breakthroughs in safety, energy density, charging speed, and lifecycle performance.
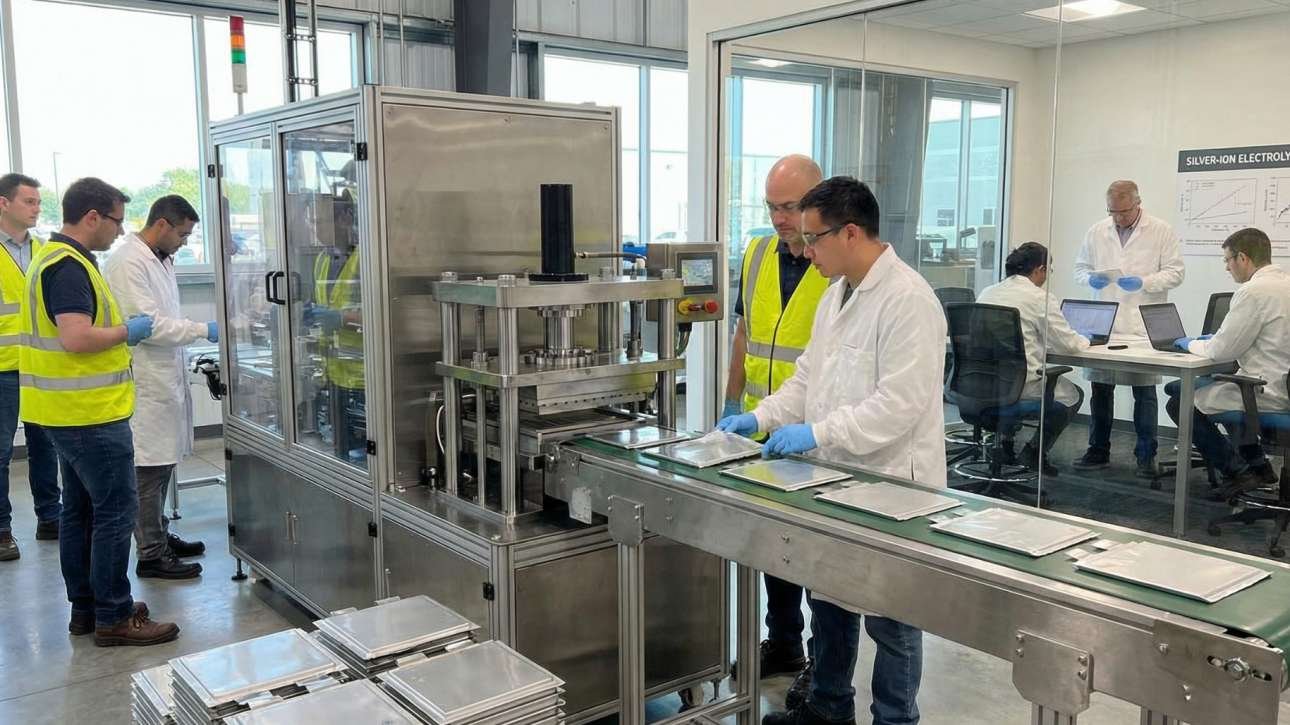
Among the most promising developments are silver solid-state batteries-a next-generation architecture that replaces liquid electrolytes with solid materials and integrates silver-based components to unlock step-change performance gains. For executives shaping long-term mobility,…
Electric vehicles are no longer an emerging trend-they are a structural force reshaping global mobility, energy systems, and industrial policy. In 2025, electric vehicles accounted for more than 25% of new vehicle sales globally, with China surpassing the 50% mark and Europe recording months where EVs outsold internal combustion vehicles entirely.
As adoption accelerates, batteries have become the true strategic battleground. In 2026, the EV battery landscape will be defined by three forces: new chemistries entering commercial use, heightened geopolitical…
FAW Hongqi’s All-Solid-State Battery Prototype Signals a Breakthrough Moment for Next-Generation EVs
In January 2026, China FAW Group reached a pivotal milestone in the global race toward next-generation electric vehicle technology. The successful rollout of Hongqi’s first all-solid-state battery prototype vehicle marks the transition of solid-state innovation from laboratory research to real-world vehicle validation-a moment with far-reaching implications for the automotive and energy storage industries.
For global automotive executives, battery manufacturers, and technology investors, this development signals more than technical progress. It reflects a strategic inflection point in how future EV platforms…
Battery technology is entering a decisive phase. As electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and grid-scale electrification accelerate globally, incremental improvements to conventional lithium-ion batteries are no longer sufficient. The next wave of competitiveness will be defined by breakthroughs in safety, energy density, charging speed, and lifecycle performance.
Among the most promising developments are silver solid-state batteries-a next-generation architecture that replaces liquid electrolytes with solid materials and integrates silver-based components to unlock step-change performance gains. For executives shaping long-term mobility,…